Difference between revisions of "Hangeul step 1"
DigitalSoju (Talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
DigitalSoju (Talk | contribs) (New Step 1) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==Step 1== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{HangeulTop}} | {{HangeulTop}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
[[File:TTMIK.png|right|link=http://www.talktomeinkorean.com]] | [[File:TTMIK.png|right|link=http://www.talktomeinkorean.com]] | ||
| − | Welcome. Unlike Japanese and Chinese, the basics of the Korean script can be learned in a matter of hours. The only way to accurately pronounce Korean words is to use the Korean script. English and Korean do not have perfectly matching sounds, so using [[Romanization]] is mostly a bad idea. | + | '''Welcome.''' Unlike Japanese and Chinese, the basics of the Korean script can be learned in a matter of hours. The only way to accurately pronounce Korean words is to use the Korean script, Hangeul (or 한글, which you will notice in the following pages is "Hangeul" written in the Korean script). English and Korean do not have perfectly matching sounds, so using [[Romanization]] is mostly a bad idea. On the following pages we have laid out a six-step lesson plan and have employed various methods to help others learn the Korean script quickly and effectively. This is a joint project between the Korean Wiki Project and [http://www.talktomeinkorean.com TalktomeinKorean.com]. We have been looking for the right voices to represent the Hangeul sounds and contributors have volunteered their time to move this project forward. We are very thankful for their effort and support. |
| − | A | + | ''A seventh step will also be created in the future to help you with advanced pronunciation.'' |
| − | ==Brief | + | ==Why Learn the Korean Alphabet?== |
| + | Some people feel that learning Romanized Korean is sufficient and do not realize how much it holds them back from becoming more skillful with Korean. Below are some simple reasons why Korean Romanization is bad. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''English sounds and Korean sounds are not the same.''' Would it make sense to try to learn English using the Korean alphabet? Especially when there are no F, V, and Z sounds in Korean? Obviously Korean does not contain all the sounds of English, and in the same sense, English does not contain all the sounds of Korean. Therefore the English alphabet cannot accurately represent the sounds of Korean. If one wants to learn English, one should learn the English alphabet and its sounds. In the same sense, if one wants to learn Korean, one should learn the Korean alphabet and its sounds. | ||
| + | *'''Korean Romanization is misleading and ambiguous.''' | ||
| + | **If one has no experience with Korean at all and uses a book with travel phrases with Romanized Korean, the pronunciation will be totally off. For example, how would you pronounce the Romanized word 'neon' ? Like 'ni-yon' or closer to 'nun'? The pronunciation is closer to 'nun' but how would you know that when its spelled like the english word 'neon?' | ||
| + | **There are various Romanization systems and sometimes it is hard to know which system one is using. For example, the gold medal Olympic skater "Kim Yuna" (김연아) is not Romanized in the traditional way, but is instead spelled closer to its English pronunciation. If it were assumed it was from the Revised Romanization System, it would sound like Yoona, not Yuna since yu represents ㅠ not ㅕ. | ||
| + | **There is no such sound as Woo and impossible to write in Korean, yet sometimes the sound ㅜ gets spelled as Woo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Brief History== | ||
''See full article at [[Wikipedia:Origin_of_Hangul|The Origin of Hangeul]]'' | ''See full article at [[Wikipedia:Origin_of_Hangul|The Origin of Hangeul]]'' | ||
[[Image:Hunmin jeong-eum.jpg|thumb|right|200px|A page from the Hunmin Jeong-eum Eonha]] | [[Image:Hunmin jeong-eum.jpg|thumb|right|200px|A page from the Hunmin Jeong-eum Eonha]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 30: | ||
{{-}} | {{-}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Basics== |
| − | + | ||
===Consonants=== | ===Consonants=== | ||
| − | + | There are 14 basic consonants in Korean and 5 double consonants which are formed from the basic consonants ㄱ, ㄷ, ㅂ, ㅅ, and ㅈ respectively. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Basic consonants |
| − | + | |[[File:Basic consonants.png]] | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | Double consonants | |
| − | | [[ | + | |[[File:Double consonants.png]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |} |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Vowels=== | |
| − | + | There are 8 basic vowel sounds along with 12 other complex vowel sounds. These complex vowels are diphthongs vowels (two vowels as one syllable). As you can also see just from looking, most of these are the combination of two basic vowels. | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |Basic vowels | |
| − | | | + | |[[File:Basic vowels.png]] |
| − | | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | |Complex vowels | |
| − | + | |[[File:Complex vowels.png]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | [[ | + | |
| − | + | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Syllable Blocks== |
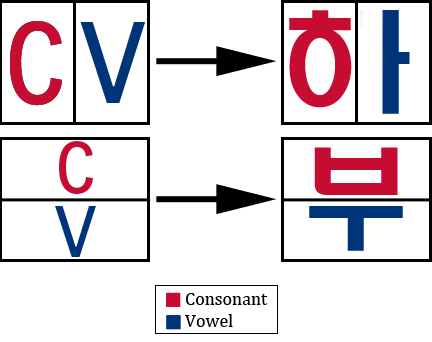
| − | Korean | + | Korean syllables are organized into blocks of letters that have a beginning consonant, a middle vowel, and an optional final consonant. A syllable block is composed of '''a minimum of two letters''', consisting of at least one consonant and one vowel. In our lesson plan, Steps 2, 3 and 4 will focus on just words with a consonant and one horizontal vowel, and words with a consonant and one vertical vowel (see below). Step 5 will introduce the final consonant and step 6 will show consonants that can consist of double vowels. |
| − | + | [[File:Syllable blocks1.png|center]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Also note if you want to write only a vowel, it must be written with the consonant [[ㅇ]], which acts as a silent placeholder for the consonant position. Why? Think of the ying and the yang concept. So if one were to want to write down the vowel ㅏ, they would have to write it as 아 with ㅇ being a silent placeholder for the consonant position. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | ==Writing== |
| − | + | Typical stroke order | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Now | + | Now we are going to start learning some letters, which are called jamo (자모). |
{| border=0 style="text-align:center; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;" | {| border=0 style="text-align:center; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;" | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 2 July 2010
Contents
Step 1
|
|
|
| Help · Cheat Sheet · Community portal |
Introduction
Welcome. Unlike Japanese and Chinese, the basics of the Korean script can be learned in a matter of hours. The only way to accurately pronounce Korean words is to use the Korean script, Hangeul (or 한글, which you will notice in the following pages is "Hangeul" written in the Korean script). English and Korean do not have perfectly matching sounds, so using Romanization is mostly a bad idea. On the following pages we have laid out a six-step lesson plan and have employed various methods to help others learn the Korean script quickly and effectively. This is a joint project between the Korean Wiki Project and TalktomeinKorean.com. We have been looking for the right voices to represent the Hangeul sounds and contributors have volunteered their time to move this project forward. We are very thankful for their effort and support.
A seventh step will also be created in the future to help you with advanced pronunciation.
Why Learn the Korean Alphabet?
Some people feel that learning Romanized Korean is sufficient and do not realize how much it holds them back from becoming more skillful with Korean. Below are some simple reasons why Korean Romanization is bad.
- English sounds and Korean sounds are not the same. Would it make sense to try to learn English using the Korean alphabet? Especially when there are no F, V, and Z sounds in Korean? Obviously Korean does not contain all the sounds of English, and in the same sense, English does not contain all the sounds of Korean. Therefore the English alphabet cannot accurately represent the sounds of Korean. If one wants to learn English, one should learn the English alphabet and its sounds. In the same sense, if one wants to learn Korean, one should learn the Korean alphabet and its sounds.
- Korean Romanization is misleading and ambiguous.
- If one has no experience with Korean at all and uses a book with travel phrases with Romanized Korean, the pronunciation will be totally off. For example, how would you pronounce the Romanized word 'neon' ? Like 'ni-yon' or closer to 'nun'? The pronunciation is closer to 'nun' but how would you know that when its spelled like the english word 'neon?'
- There are various Romanization systems and sometimes it is hard to know which system one is using. For example, the gold medal Olympic skater "Kim Yuna" (김연아) is not Romanized in the traditional way, but is instead spelled closer to its English pronunciation. If it were assumed it was from the Revised Romanization System, it would sound like Yoona, not Yuna since yu represents ㅠ not ㅕ.
- There is no such sound as Woo and impossible to write in Korean, yet sometimes the sound ㅜ gets spelled as Woo.
Brief History
See full article at The Origin of Hangeul
Hangeul was introduced under Sejong the Great and finished around 1444. Up until and even after that time, Chinese characters were used as the written language, limiting reading and writing to the royal and government elite. King Sejong wanted Korea to have its own script that could be easily learned by anyone--even commoners. After its creation, Hangeul was said to be easy enough to learn that a wise man could finish it in the morning and a fool could finish it by night. For this reason there was opposition to Hangeul for a time by Korean aristocrats, believing only those of social superiority should have the privilege of learning to read and write.
Ever since Hangeul was first introduced, it went through many phases of refinement. Korean went through a large reformation during the Japanese colonization in the early 1900's, removing many of the now-archaic letters and changing several rules.
For more information on Hangeul, check out this wikipedia article.
For those interested in learning Korean Sign Language (KSL), please see the page on sign language.
Basics
Consonants
There are 14 basic consonants in Korean and 5 double consonants which are formed from the basic consonants ㄱ, ㄷ, ㅂ, ㅅ, and ㅈ respectively.
| Basic consonants | 
|
| Double consonants |
Vowels
There are 8 basic vowel sounds along with 12 other complex vowel sounds. These complex vowels are diphthongs vowels (two vowels as one syllable). As you can also see just from looking, most of these are the combination of two basic vowels.
| Basic vowels | 
|
| Complex vowels | 
|
Syllable Blocks
Korean syllables are organized into blocks of letters that have a beginning consonant, a middle vowel, and an optional final consonant. A syllable block is composed of a minimum of two letters, consisting of at least one consonant and one vowel. In our lesson plan, Steps 2, 3 and 4 will focus on just words with a consonant and one horizontal vowel, and words with a consonant and one vertical vowel (see below). Step 5 will introduce the final consonant and step 6 will show consonants that can consist of double vowels.
Also note if you want to write only a vowel, it must be written with the consonant ㅇ, which acts as a silent placeholder for the consonant position. Why? Think of the ying and the yang concept. So if one were to want to write down the vowel ㅏ, they would have to write it as 아 with ㅇ being a silent placeholder for the consonant position.
Writing
Typical stroke order
Now we are going to start learning some letters, which are called jamo (자모).

|