Hangeul step 1
|
|
|
| Help · Cheat Sheet · Community portal |
Brief history
Hangul was introduced under Sejong the Great and finished around 1444. Up until and even after that time, Chinese characters were used as the written language which limited reading and writing to the royal and government elite. King Sejong wanted Korea to have it's own script which was easier for the commoner to use. Hangeul was said to be easy enough to learn that a wise man could finish it in the morning and a fool could finish it by night. For that reason, there was opposition to Hangeul for a long time by the aristocrats who thought learning Hangeul was only for Women or the poor.
Hangeul is the only alphabet in existence that was invented from scratch for an existing language, rather than naturally developed.
Every since Hangeul was first introduced, it went through many phases of being refined. Korean went through a large reformation during the Japanese colonization in the early 1900's, removing many of the now archaic letters and changing some rules.
Jamo
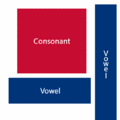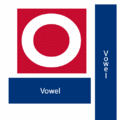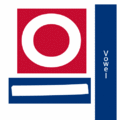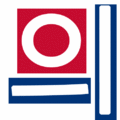
Korean is very differentiated from the other Asian languages in that it uses letters (called Jamo) that are arranged in character form. Just like English, Jamo are classified as either consonants or vowels.
Consonants
There are three kinds of consonants. The 10 simple consonants form the basis of the other consonants. The 5 tense consonants (also known as double or glottalized) are written as two simple consonants and involve tensing up the mouth. The 4 aspirated consonants (sometimes listed with the simple) involve blowing more air than the simple consonant it's based on.
Vowels
There are simple and complex vowels. The 6 simple vowels form the basis of the complex vowels. Within the complex vowels there are diphthongs and iotized. Diphthongs usually (but not always) add a 'w' sound onto a simple vowel and the iotized always adds a 'y' sound.
Structure
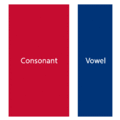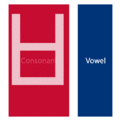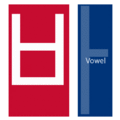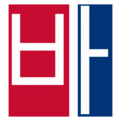
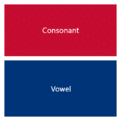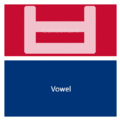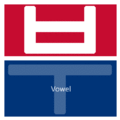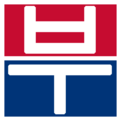
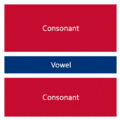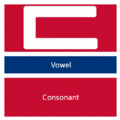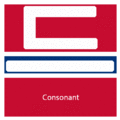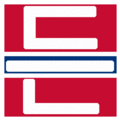
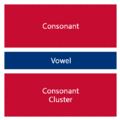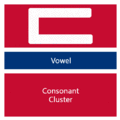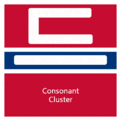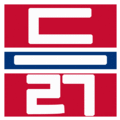
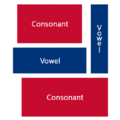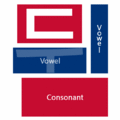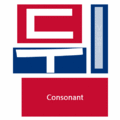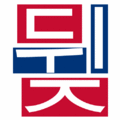
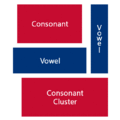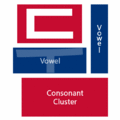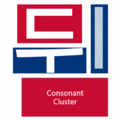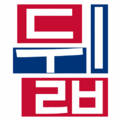
The easiest way to describe the structure of Hangeul is that it's a combination of a letter-based language like English and a character-based language like Chinese. Korean syllables are organized into blocks of Jamo that have a beginning consonant (called Cho), a middle vowel (called Jung), and an optional end consonant (called Jong).
- ㄱ+ㅏ = 가 (g+a = ga)
- ㄴ+ㅜ+ㄴ=눈 (n+oo+n = noon)
Syllable combinations (under construction)